Analytical Instrumentation
Determination of water content within battery materials using coulometric Karl Fischer titration
Sep 20 2022
The accurate determination of water content within lithium-ion batteries is of key importance, an excess of water can cause degradation of the electrolyte and leads to the formation of certain by products which significantly lower the lifespan and capacity of the battery, the most prominent form of by-product is hydrofluoric acid. Due to this, the water content within lithium-ion batteries and related battery materials must be kept to a minimum.
The most common test for water content within battery materials is via coulometric Karl Fischer titration. Using a coulometric Karl Fischer allows you measure water content to level of 1 part per million. Due to the different elements of the composition of a lithium battery, different sample introduction techniques must be used for different elements.
Water content within liquid electrolytes can be simply analysed using a direct injection coulometric titrator, such as the Aquamax KF Plus, or Aqua 40 basic system from ECH Elektrochemie Halle - ECH - Aquamax KF Plus – Using the direct injection technique a small amount of sample will be directly injected via syringe into the Karl Fischer titration cell, once entered into the cell the reaction will allow water content determination down to 1 part per million. By directly injection the sample, all contact with the atmosphere will be avoided, meaning the hygroscopic properties of the electrolyte will not absorb any water from the surrounding atmosphere, only the true water content is analysed.
The water determination for powdered, gel or liquid battery materials can be realised using a coulometric Karl Fischer coupled with the principle of headspace technology with a closed loop carrier gas, as featured in the Aqua 40 Vario ECH - AQUA 40.00 Vario – Using this principle the battery sample is placed into a closed headspace vial and heating between 35-300 degrees C (depending on sample composition) during this heating phase, the water will be extracted and transported using a dry carrier gas into the titration cell where the coulometric reaction occurs, again allowing for ppm analysis of battery materials.
ECH also provides solutions for the testing of LiCoO2, the compound commonly used in the positive electrodes of lithium-ion batteries. LiCoO2 requires high temperature solutions for the desorption of the water content and therefore a modification of the headspace technique must be used. The Aqua 40.00 HTO allows for temperature heating of up to 1300 degrees C, typically 200-800 degrees C is required for LiCoO2 analysis.
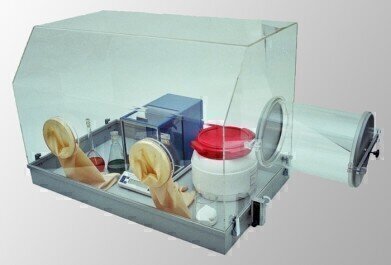
Atmospheric protection is also critical in the handling battery materials in preparation for sample analysis. The hygroscopic nature of these samples mean moisture can be easily absorbed into the sample. This would mean all sample analysis runs provide higher results than required. To combat this, sampling should be done in hermetically sealed environment. The GloveBox from ECH allows for sample preparation in a dry, hermetically sealed atmosphere. The instrument, analytical balance and preparation tools can all be placed into the GloveBox. In case of direct dosing, such as the Aquamax KF Plus, the measuring device is placed in the GloveBox, eliminating any possible hygroscopic/atmospheric interference. ECH - GloveBox
For more information on the ECH advantage when analysing lithium batteries and related materials please contact us today or visit our website.
Digital Edition
PIN 25.3 June/July
June 2024
Analytical Instrumentation - Recent Advances In Various Bench Scale Accelerated Oxidative Testing Methods For Fuels - Petrochemical Industry: Anton Paar Solutions Streamline Processes, Reduce H...
View all digital editions
Events
Jul 30 2024 Jakarta, Indonesia
Jul 30 2024 Jakarta, Indonesia
China Energy Summit & Exhibition
Jul 31 2024 Beijing, China
Jul 31 2024 Chengdu, China
Aug 05 2024 Moon Township, PA, USA