-
 Figure One DVLS SimDist analyser
Figure One DVLS SimDist analyser -
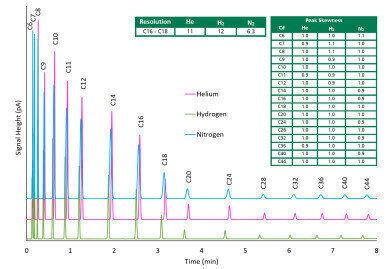 Figure Two SimDist resolution and skwewnes
Figure Two SimDist resolution and skwewnes -
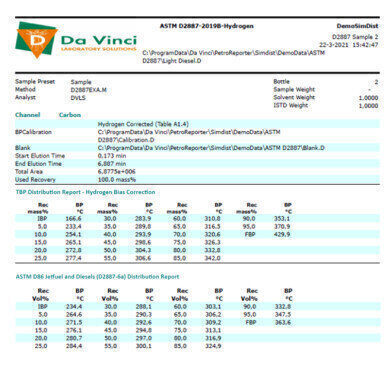 Figure Three SimDist PetroReporter
Figure Three SimDist PetroReporter
Analytical Instrumentation
Use of Hydrogen & Nitrogen as Alternative Carrier Gases for SimDist ASTM D 2887
Apr 20 2021
Traditionally Helium is used as a carrier gas for a SimDist analysis. In 2018 ASTM revised the D2887 method to allow the use of Hydrogen and Nitrogen as an alternative carrier gas. When using Hydrogen or Nitrogen a bias correction for the obtained results is required. Da Vinci Laboratory Solutions evaluated the performance of the DVLS Mid-Range SimDist Analyser using the alternative carrier gases Hydrogen & Nitrogen and published the results in a new application note.
SimDist D2887 Configuration
The DVLS Mid-Range SimDist analyser uses an Agilent 8890 GC configured with the DVLS Programmed Temperature Inlet, Flame Ionization Detector, AutoSampler and an ASTM D2887 application kit. The DVLS PetroReporter software is used to calculate the performance parameters and boiling point distribution conform the ASTM D2887 method.
Experimental testing
The analysis is performed according to procedure B of the ASTM D2887 method using three different carrier gases. For each carrier gas the system is validated according to the method using one validation sample and two Gas Oil samples, of which one Gas Oil sample contains FAMEs.
The analysis results of all three carrier gases pass the criteria for validation, resolution and skewness specifications as described in ASTM D2887 Procedure B. Figure Two shows the overlay of time calibration standard of the three different carrier gases combined with the found resolution and peak skewness. These tests demonstrate that Nitrogen & Hydrogen can be used as carrier gas while complying with the official ASTM D2887 method specifications.
To check if the results determined with the alternative gases are significantly comparable to those obtained with Helium, a paired t-test is performed based on eight replicate measurements for each carrier gas. This test is carried out before and after a bias correction.
Bias correction is performed on Hydrogen and Nitrogen according to ASTM D2887-19aε1 Table A.1.4 (H2) and Table A.1.8 (N2). The DVLS PetroReporter software is used to apply the bias correction for the different carriers and correlate the results to ASTM D86. Figure Three shows a sample report for the carrier gas Hydrogen generated with DVLS PetroReporter including the correlated ASTM D86 results.
In this experiment all the calculated t-values, with bias correction, are lower than the critical value of 2.228. The application note provides all details of the analysis results and the calculated t-values.
Conclusion of the Carrier Gas Evaluation
The analysis results of various validation and reference samples demonstrate that the analyser complies with the ASTM D2887 specifications for the validation, resolution and peak skewness criteria for all three carrier gases without the need for a bias correction. The ASTM D2887 method describes a bias correction for alternative carriers. Evaluating the analysis results before and after bias correction shows that there is no significant difference between Helium and bias corrected Hydrogen and Nitrogen.
Digital Edition
PIN 25.4 Aug/Sept
September 2024
Analytical Instrumentation - Novel and Rapid LSC method for the analysis of biogenic carbon in fuels Measurement and Testing - Matrix evaluation on the Xplorer-V with Vectra autosampler accordi...
View all digital editions
Events
Sep 23 2024 New Orleans, LA, USA
Sep 23 2024 Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Sep 24 2024 Kielce, Poland
Sep 24 2024 Calgary, Canada
IDW DOWNSTREAM CONFERENCE 2024
Sep 24 2024 Warsaw, Poland


















